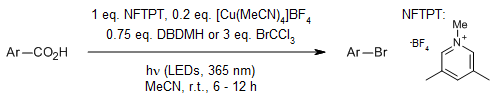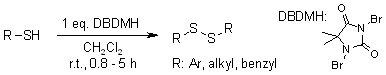1,3-Dibromo-5,5-Dimethylhydantoin, DBDMH
Product Manager:Nick Wilde
.jpg?access_token=e8b9b546-c34c-4f6e-8516-46d61dd3e881)
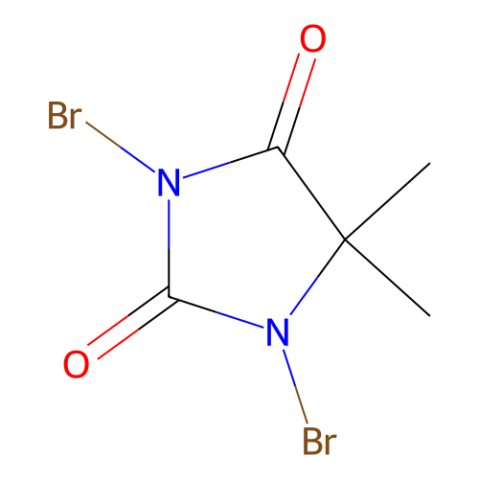
DBDMH is a cheap and convenient alternative to NBS (N-bromosuccinimide) for example for the bromination of electron-rich arenes.
Recent Literature

A copper catalyst system utilizing a chiral bisoxazoline ligand catalyzes the asymmetric oxidative desymmetrization of easily obtainable 2-(hetero)aryl- and alkyl-substituted glycerols, utilizing 1,3-dibromo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin and methanol. This process efficiently produces a range of glycerate derivatives in high yields and with excellent enantioselectivities.
K. Yamamoto, Y. Suganomata, T. Inoue, M. Kuriyama, Y. Demizu, O. Onomura, J. Org. Chem., 2022, 87, 6479-6491.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.2c00398

A straightforward thiourea catalyst, in conjunction with 1,3-dibromo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin as a cost-effective and stable halogen source, facilitated the stereospecific dibromination of various functionalized alkenes at room temperature. This method was also adaptable to alkynes and aromatic rings, and could be extended to dichlorination reactions by utilizing the 1,3-dichloro hydantoin derivative.
G. Hernández-Torres, B. Tan, C. F. Barbas III, Org. Lett., 2012, 14, 1858-1861.
https://doi.org/10.1021/ol300456x
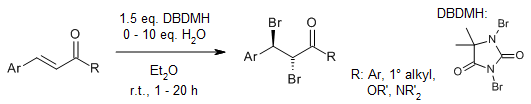
A mild and catalyst-free process allows for the direct 1,2-dibromination of alkenes using 1,3-dibromo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin (DBDMH) as the bromine source. This method converts various alkene substrates into their corresponding 1,2-dibrominated products in high yields and with exclusive diastereoselectivity, without the need for an external oxidant.
L. Wang, L. Zhai, J. Chen, Y. Gong, P. Wang, H. Li, X. She, J. Org. Chem., 2022, 87, 3177-3183.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.1c02906
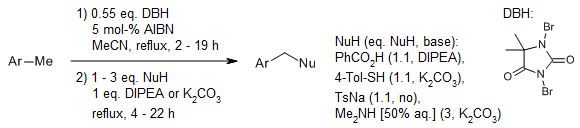
When methylarenes are treated with either 1,3-dibromo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin or N-bromosuccinimide, along with a catalytic quantity of 2,2′-azobis(isobutyronitrile), and subsequently reacted with a nucleophile like benzoic acid, p-toluenethiol, sodium p-toluenesulfinate, aqueous dimethylamine, or succinimide, the corresponding benzylated products are obtained in good yields.
H. Shimojo, K. Moriyama, H. Togo, Synthesis, 2015, 47, 1280-1290.
https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1380069
A catalytic decarboxylative halogenation process is capable of accommodating a wide range of (hetero)aryl carboxylic acid substrates. The intermediate aryl radical produced can undergo two different functionalization pathways: (1) atom transfer to produce bromo- or iodo(hetero)arenes, or (2) radical capture by copper followed by reductive elimination to yield chloro- or fluoro(hetero)arenes.
T. Q. Chen, P. Scott Pedersen, N. W. Dow, R. Fayad, C. E. Hauke, M. S. Rosko, E. O. Danilov, D. C. Blakemore, A.-M. Dechert-Schmitt, T. Knauber, F. N. Castelano, D. W. C. MacMillan, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 8296-8305.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.2c02392
Using 1,3-dibromo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin (DBDMH) as the oxidant, a gentle and effective method is available for oxidizing various thiols to their corresponding disulfides, either in solution or under solvent-free conditions.
A. Khazaei, M. A. Zolfigol, A. Rostami, Synthesis, 2004, 2959-2961.
https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2004-834919
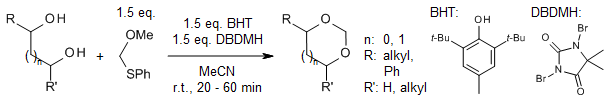
A gentle and effective method allows for the synthesis of methylene acetals from 1,2- and 1,3-diols, utilizing methoxymethylphenylsulfide, 1,3-dibromo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin (DBDMH), and dibutylhydroxytoluene (BHT) as a stabilizing agent. The incorporation of BHT minimizes side reactions and promotes high-yield production of methylene acetals from a range of diols, including those of carbohydrate nature.
T. Maegawa, Y. Koutani, K. Otake, H. Fujioka, J. Org. Chem., 2013, 78, 3384-3390.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jo4000256
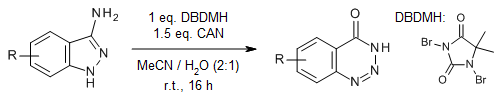
At room temperature, an oxidative rearrangement of 3-aminoindazoles yields diversely functionalized 1,2,3-benzotriazine-4(3H)-ones in good yields. The use of water as a cosolvent aids in the halogen-induced ring expansion of 3-aminoindazoles under oxidative conditions.
Y. Zhou, Y. Wang, Y. Lou, Q. Song, Org. Lett., 2018, 20, 6494-6497.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.8b02813
Quoted from:https://www.organic-chemistry.org/chemicals/oxidations/dbdmh-1,3-dibromo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin.shtm
Aladdin:https://www.aladdinsci.com