General Conjugation Protocols of PEG linkers——PEG Amine
Polyethylene glycol (PEG) linker is a chemical sensing the carrier of polyethylene glycol (PEG), due to its solubility in water and non-immunogenicity. In the field of scientific research, it is widely used in chemical coupling, drug delivery, nanoparticles functionalized modifications and chemical biology. Its powerful function has attracted intense research interest. In the following, we will show the general conjugate reactions of nine common polyethylene glycol linkers one by one.
PEG Amine
Coupling Reaction of PEG amine with NHS ester
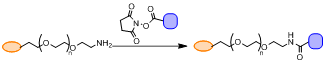
Reaction condition 1: , , , ; bases: TEA,
Reaction condition 2: PBS buffer, Borate buffer, Carbonate buffer, pH 8.5
1) Under continuous stirring, NHS-containing compound was added to the above reaction mixture 1:1 or 2:1 equivalent by mmol depending on the reaction kinetics.
2) The reaction mixture was stirred for 3-24 hours depending on the substrate properties, monitored either by LC-MS or TLC plate.
3) The final product can be isolated by general organic synthesis workup or by column purification.
Coupling Reaction of acid to amine-PEG
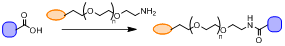
Reaction condition: (or DCC, HATU, etc.), DMF, (or CH2Cl2, DMSO, THF), bases: TEA (or DIPEA, Py)
1) Equilibrate and carboxylic acid to room temperature before opening bottles.
2) Prepare carboxylic acid stock solutions by dissolving 100 mg of each reagent (~100 µL) in the desired amount of dry water-miscible solvent (e.g., DMF or DMSO).
3) Cap, store and handle stock solutions as directed in the Important Product Information Section.
4) Add appropriate amounts of and amine-containing molecule to the appropriate amount of carboxylated surface in activation buffer and react for 15 minutes at room temperature.
5) Add DTT to quench the . Note: For surfaces that can be easily washed, the quenching step can be skipped, and the surface washed with Coupling Buffer to remove any remaining and NHS.
6) Add the carboxylic acid mixture prepared in Conjugation Buffer to the activated surface and react for 2 hours at room temperature.
7) To quench the reaction, add hydroxylamine or another amine-containing buffer. Hydroxylamine hydrolyzes nonreacted NHS on the solid surface and results in hydroxamate formation. Other quenching methods involve adding Tris, lysine, glycine or ethanolamine; however, these primary amine-containing compounds modify carboxyls. (Note: The newly introduced carboxy groups can be further modified by repeating Steps 4 and 5)
8) Add the desired amine-containing substrate, prepared in Coupling Buffer, to the activated surface and react for 2 hours at room temperature.
9) Quench the reaction as described in Step 7.
General Procedure for acid with amine-PEG in MES buffer
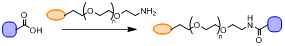
Reaction condition: 0.5 M MES buffer pH 5.5; ·HCl, NHS
RCOOH (1 mmol) is dissolved in 0.5 M MES pH 5.5 buffer (1 mL); (1.2 mmol) is added to the solution and the reaction is stirred for 10 min. Subsequently, NHS (10 mmol) is added to the reaction. The reaction is left to stir at RT for 60 min. Amine-PEG (2 mmol) is then added, and the reaction is stirred for 12 h at RT.
