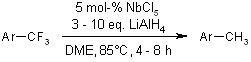LAH, Lithium aluminum hydride, Lithium tetrahydridoaluminate
Product Manager
Sandra Forbes

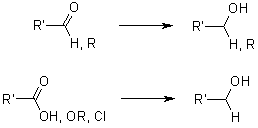
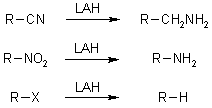
LiAlH4 is a highly prevalent and potent reducing agent capable of reducing a wide array of diverse functional groups.
Recent Literature
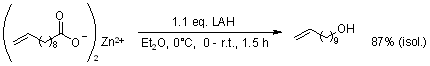
A method for synthesizing alkenyl halides of any length from cost-effective starting materials has been reported. By utilizing standard organic transformations, high overall yields of straight-chain α-olefin halides were achieved without any observable olefin isomerization, and all unreacted starting materials were fully recovered.
T. W. Baughman, J. C. Sworen, K. B. Wagener, Tetrahedron, 2004, 60, 10943-10948.
DOI: 10.1016/j.tet.2004.09.021
A tethered alkene moiety serves as an invisible directing group in zirconium-catalyzed reductive cleavage of Csp3 and Csp2 carbon-heteroatom bonds, encompassing C-O, C-N, and C-S bonds. This reaction is particularly advantageous for the cleavage of homoallylic ethers and the elimination of terminal allyl and propargyl groups.
C. Matt, F. Kölblin, J. Streuff, Org. Lett., 2019, 21, 6909-6913.
DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.9b02572
Secondary α-chloroketimines undergo reaction with lithium aluminium hydride in ether, leading to a mixture of cis- and trans-1,2,3-trisubstituted aziridines via nucleophilic addition of hydride across the imino bond, followed by intramolecular nucleophilic substitution. Similarly, tertiary α-chloroketimines react to produce 1,2,2,3-tetrasubstituted aziridines. In contrast, α,α-dichloroketimines react stereospecifically to yield exclusively cis-aziridines.
N. De Kimpe, L. Moens, Tetrahedron, 1990, 46, 2965-2974.
DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4020(01)88388-5
A methylation reagent, followed by lithium aluminum hydride, effectively reduces a wide range of phosphine oxides. Notably, optically active P-chirogenic phosphine oxides undergo reduction with inversion of their configuration.
T. Imamoto, S.-i. Kikuchi, T. Miura, Y. Wada, Org. Lett., 2001, 3, 87-90.
DOI: 10.1021/ol0068041
In the presence of LDA, phenol carbamates undergo an anionic ortho-Fries rearrangement to form their corresponding amides. For sterically hindered substrates, conversion can be achieved using s-BuLi/TMEDA at -90°C. These amides can then be efficiently reduced to the corresponding Mannich bases using lithium aluminum hydride.
N. Assimomytis, Y. Sariyannis, G. Stavropoulos, P. G. Tsoungas, G. Varvounis, P. Cordopatis, Synlett, 2009, 2777-2782.
In the presence of 5 mol% niobium(V) chloride, trifluoromethyl arenes undergo reduction with lithium aluminum hydride to yield toluene derivatives in good yields. Additionally, the stepwise partial reduction of a bis(trifluoromethyl) arene has been demonstrated.
K. Fuchibe, Y. Ohshima, K. Mitomi, T. Akiyama, Org. Lett., 2007, 9, 1497-1499.
DOI: 10.1021/ol070249m
When substituted arylbromides are treated with tert-butyllithium in diethyl ether at -78˚C and subsequently added to dichlorodiethoxysilane, diaryldiethoxysilanes are formed quantitatively. By stirring these diaryldiethoxysilanes with lithium aluminum hydride in diethyl ether, they can be reduced to the corresponding diarylsilanes. This approach circumvents the need to handle gaseous and explosive dichlorosilane.
P. Gigier, W. A. Herrmann, F. E. Kühn, Synthesis, 2010, 1431-1432.
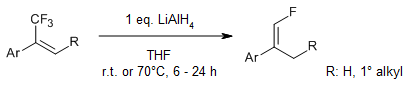
The stereoselective hydrodefluorination of trifluoromethylated alkenes with LiAlH4 yields terminal monofluoroalkenes in excellent yields and diastereoselectivities. Mechanistic investigations indicate that the reaction proceeds through a hydroalumination step, followed by a stereoselective fluoride elimination.
P. Poutrel, X. Pannecoucke, P. Jubault, T. Poisson, Org. Lett., 2020, 22, 4858-4863.
DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c01701
Quoted from: https://www.organic-chemistry.org/chemicals/reductions/lithiumaluminumhydride-lah.shtm
Aladdinsci: https://www.aladdinsci.com