Method and Precautions of SDS-PAGE Gel Preparation
Product Manager:Harrison Michael

SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) is a commonly used technique to separate proteins based on size. By denaturating the protein and giving it a uniform negative charge, the protein migrates to the positive pole under the application of an electric field and is separated according to size. In this paper, the preparation method of SDS-PAGE gel, common problems and solutions will be introduced in detail.
I. SDS-PAGE Gel Preparation
* Note:
Acrylamide and diacrylamide are neurotoxins and should be handled with appropriate personal protective equipment. The total volume is usually 10 mL but can be adjusted as needed.
Ammonium persulfate (APS), as an initiator, can accelerate the polymerization reaction when used with TEMED.
The volume of the buffer was adjusted for the volume of acrylamide and diacrylamide to ensure the accuracy of the total volume.
These formulations are based on commonly used separation gel concentrations, and specific experiments may need to be adjusted according to the molecular weight range of the target protein.
1. Preparation of separation glue
(1) Formula Table:
The following table lists the formulations of the different concentrations of the separation glue:
|
(2) Preparation steps:
1. Clean the glass plate and gasket:
• Thoroughly clean glass plates and spacers using deionized water and ethanol to ensure there are no residues.
2. Assemble the glass plate:
• Check the integrity of the glass plate by assembling the glass plate on a stable, uniform surface using gaskets, ensuring that the lock clamps are assembled.
3. Prepare separation glue solution:
Combine water, 30% acrylamide, 1.5 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.8), 10% SDS, 10% APS, and TEMED in the recipe table in a dry, clean beaker. TEMED must be the last ingredient added.
• After mixing well, pour into the assembled glass plate immediately to ensure even distribution.
• Cover the gel surface with water or isopropanol to maintain a homogeneous surface and solidify for about 20 to 30 minutes at room temperature.
2. Preparation of concentration glue
(1) Formula Table:
The following table lists the formula for the concentrated glue:
|
(2) Preparation steps:
1. Clean the glass plate and gasket:
• Thoroughly clean glass plates and spacers using deionized water and ethanol to ensure there are no residues.
2. Assemble the glass plate:
• Check the integrity of the glass plate by assembling the glass plate on a stable, uniform surface using gaskets, ensuring that the lock clamps are assembled.
3. Preparation of concentrated glue solution:
Combine water, 30% acrylamide, 0.5 M Tris-HCl (pH 6.8), 10% SDS, 10% APS, and TEMED in the recipe table in a dry, clean beaker. TEMED must be the last ingredient added.
• After mixing well, pour into the assembled glass plate immediately to ensure even distribution.
• Cover the gel surface with water or isopropanol to maintain a homogeneous surface and solidify for about 20 to 30 minutes at room temperature.
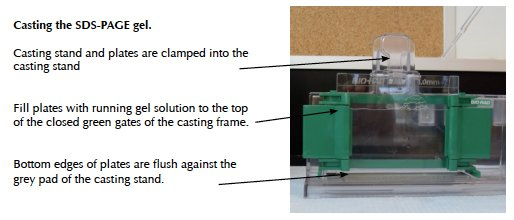
II. Problems and solutions
During SDS-PAGE gel preparation, various problems may be encountered. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
1. Glue leakage problem:
• Cause: The glass plate is not aligned or defective, and the gasket has poor airtightness.
• Solution: Make sure the glass plate is dry, lock the clamp after alignment, and check the integrity of the glass plate.
2. Gel does not solidify:
Cause: APS or TEMED failure, improper operation
• Solution: Use fresh APS to ensure that the TEMED is not spoiled and to avoid shaking before the glue is not set.
3. Uneven gel solidification:
• Reason: The glass plate was not washed, the reagent was precipitated, and the mixture was not uniform.
• Solution: Wash the glass plate thoroughly to ensure that the reagent is clear and the components are evenly mixed.
4. Bubbles in the gel:
• Reason: material problem of rubber pad, improper insertion of comb.
• Solution: Use a solid soft rubber pad or plastic wrap and insert the comb correctly.
5. Upper glue edge defect:
• Reason: glass plate edge strip poor airtight.
• Solution: Check and replace the edge strips to ensure their airtightness.
6. After pulling the comb, there is glue in the lane:
Cause: Excessive use of TEMED
• Solution: Reduce the amount of TEMED used and ensure that the glue is not partially set before inserting the comb.
7. Swim lane skew after pulling comb:
• Cause: The comb does not match the glass plate.
• Solution: Make sure the comb matches the glass plate and replace it if necessary.
8. "Leakage sample" appeared in the upper gel electrophoresis:
• Reason: the glass plate is partially separated from the glue, and the loading buffer problem.
• Solution: Carefully remove the glass plate to avoid separation and avoid inserting the gun tip too deep when loading the sample.
9. Lane center depression:
• Cause: Too long exposure of glue to the air after comb insertion.
• Solution: Try to insert the comb within 25 minutes to avoid prolonged exposure.
Conclusion
By understanding the preparation method of SDS-PAGE gel and the solutions to common problems in detail, the experimenter can effectively improve the success rate of the experiment, reduce the error operation, and obtain high-quality experimental results. A piece of high-quality SDS-PAGE gel can lay the foundation for protein electrophoresis, so as to run out of clear and good-looking bands and obtain high-quality experimental results. Welcome to purchase high-quality reagents in Aladdin, and get high-quality results with high-quality reagents.
Aladdin:https://www.aladdinsci.com/
