Scenarios of application of different preparation methods for peripheral blood
After peripheral blood samples are collected, we need to extract the single cells to be tested from them. There are two most commonly used sample preparation methods for peripheral blood samples:
I. Erythrocyte lysis method
Utilizing an erythrocyte lysing solution to remove the red blood cells
ii. Ficoll method
Gradient density centrifugation utilizing the difference in sedimentation coefficients of different cells to extract PBMCs
Erythrocyte lysis method
The lysed red method, in which the red blood cells in the sample are lysed. There are 10-100 times more red blood cells than white blood cells in the blood, and an excessive number of red blood cells can affect the analysis of the cell population. Therefore, we often need to lyse red blood cells when doing blood sample testing.
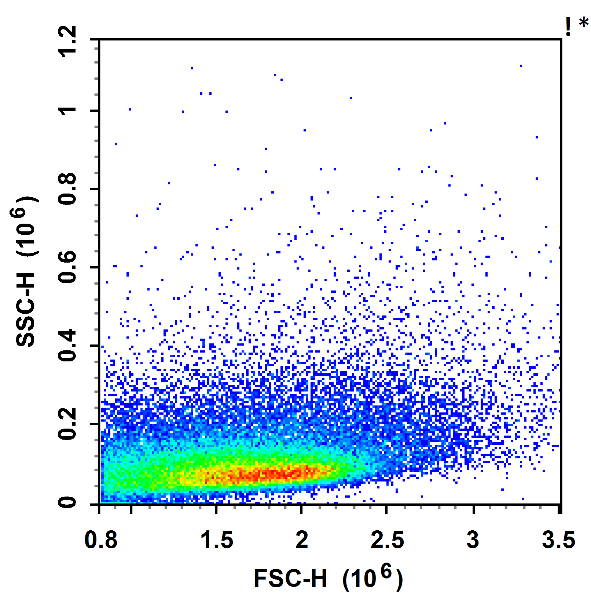
pre-reddening
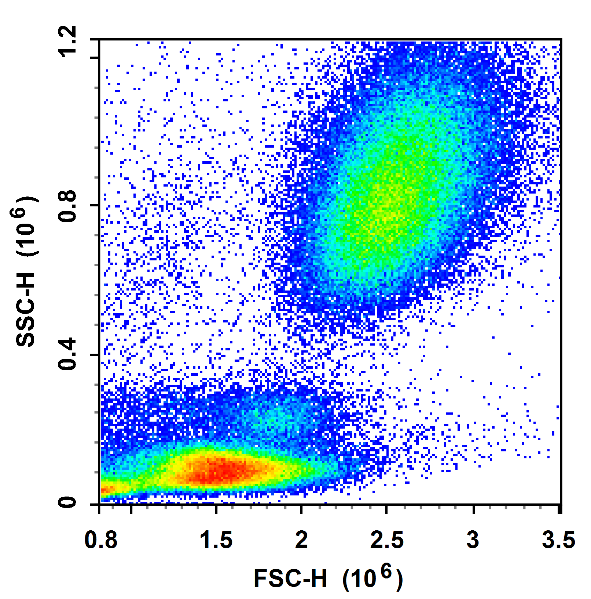
post-reddening
01 Principle
Destruction of the structure of red blood cells by altering the osmotic pressure and ionic concentration of the extracellular environment. The chemicals in erythrocyte lysates typically include one or more lysing enzymes, such as hemoglobinases. These enzymes bind to specific proteins on the red blood cell membrane, thereby lysing the red blood cell membrane and releasing the contents of the cell.
02 Advantages
⊙ Complete preservation of all types of white blood cells (lymphocytes, monocytes, granulocytes, etc.)
⊙ High yield
⊙ Simple 10-minute procedure
03 Disadvantages
⊙ Higher time requirements for red cracking, either too long or too short can affect results
⊙ Lower cell activity than Ficoll
04 Precautions for use
⊙ Longer lysis times can cause damage to other cells, so it is important to be sure of the lysis time;
⊙ Not all blood samples need to be lysed for flow-through testing. ⊙ Not all blood samples need to be lysed for flow-through testing. If white blood cells (e.g., lymphocytes, monocytes, granulocytes, etc.) are to be tested, red blood cells need to be lysed; if red blood cells are to be tested, red blood cells do not need to be lysed;
⊙ If the subsequent sample is not to be used for flow analysis, but is to be cultured or cryopreserved for resuscitation, the activity of cells cultured using lysed erythrocytes may be compromised.
There are two types of erythrocyte lysates currently available on the market: with fixative; and without fixative.Erythrocyte lysates without immobilizers are milder in action; those with immobilizers are more aggressive, but are more effective at lysing red blood cells.
Care should be taken when using fixative-containing erythrocyte lysates:
a. Fixatives may reduce the fluorescence signal intensity of antibodies, especially tandem dyes;
b. Also, if the cells are fixed prior to staining, antigenic epitopes may be disrupted by fixation, resulting in unrecognized antibodies.
Ficoll Density Gradient Centrifugation
01 Principle
Cells are separated with the help of cell separation solution and centrifugation operation based on the difference in sedimentation coefficients of the cells.
02 Advantages
⊙ Pure cells for detection of intracellular factors after cell culture
⊙ Cells can be frozen and then resuscitated, cultured, and assayed
⊙ Removal of dead cells
03 Disadvantages
⊙ Complexity of the procedure, requiring more than 30 min.
⊙ Extensive experience is required to remove the white membrane layer
⊙ only lymphocytes and monocytes can be obtained and some rare cells are lost
⊙ May cause cellular receptor activation
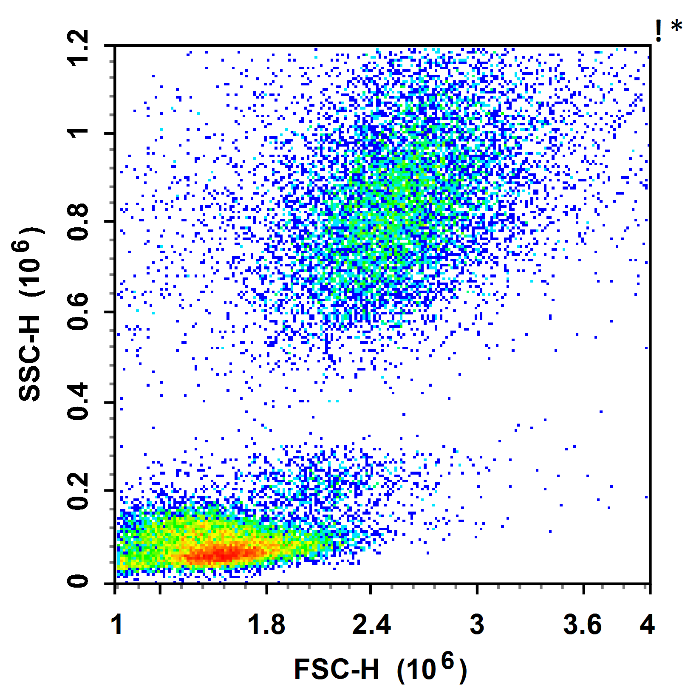
pre-separation
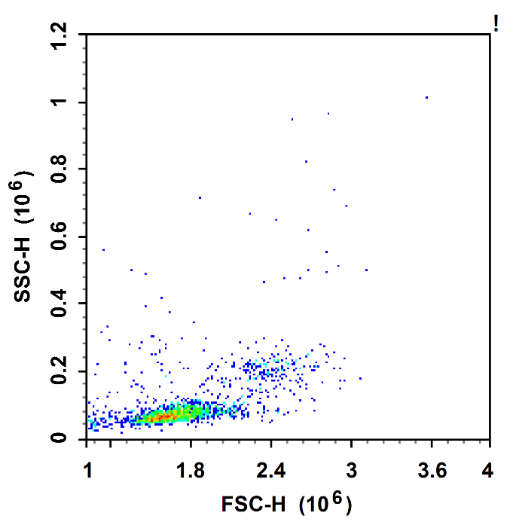
post-separation
summarize
• It is recommended that peripheral blood samples be prepared using the split-red method if the subject of the study is lymphocytes, monocytes or granulocytes and the cells are not to be cultured or frozen, but are to be analyzed only by flow-through analysis;
• If the subject of the study is a lymphocyte subpopulation or monocytes, it is recommended that the Ficoll method be used to extract PBMCs when performing the following experiments:
(1) The obtained cells need to be continued to be cultured, stimulated, blocked or frozen;
(2) Study of monocytes. Because mononuclear cells make up only 3-10% of leukocytes, the cell population will be found to be too small if the split-red method is used. To ensure adequate sample size, the Ficoll method is required.
For more information, visit our website: www.aladdinsci.com.
