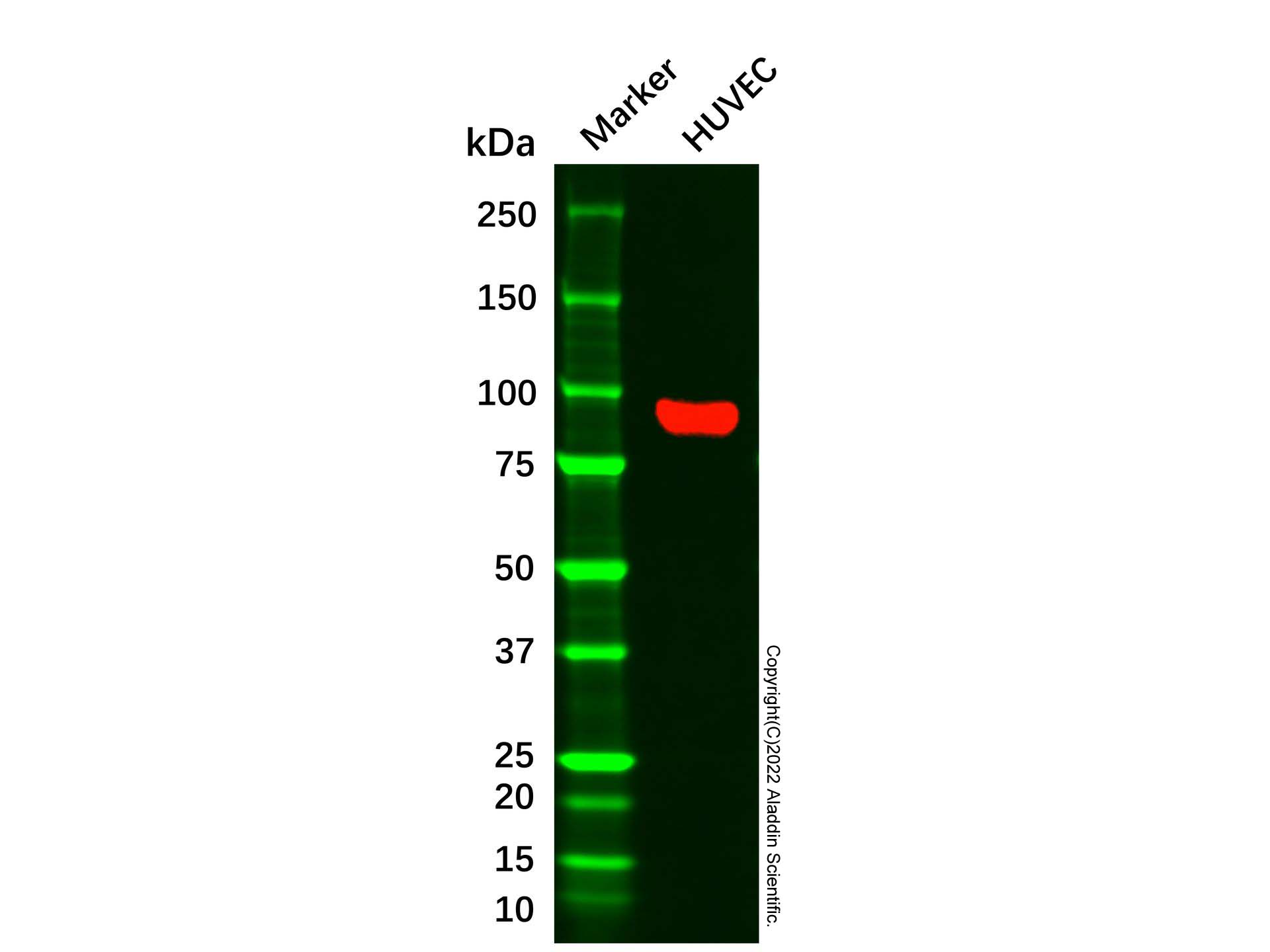
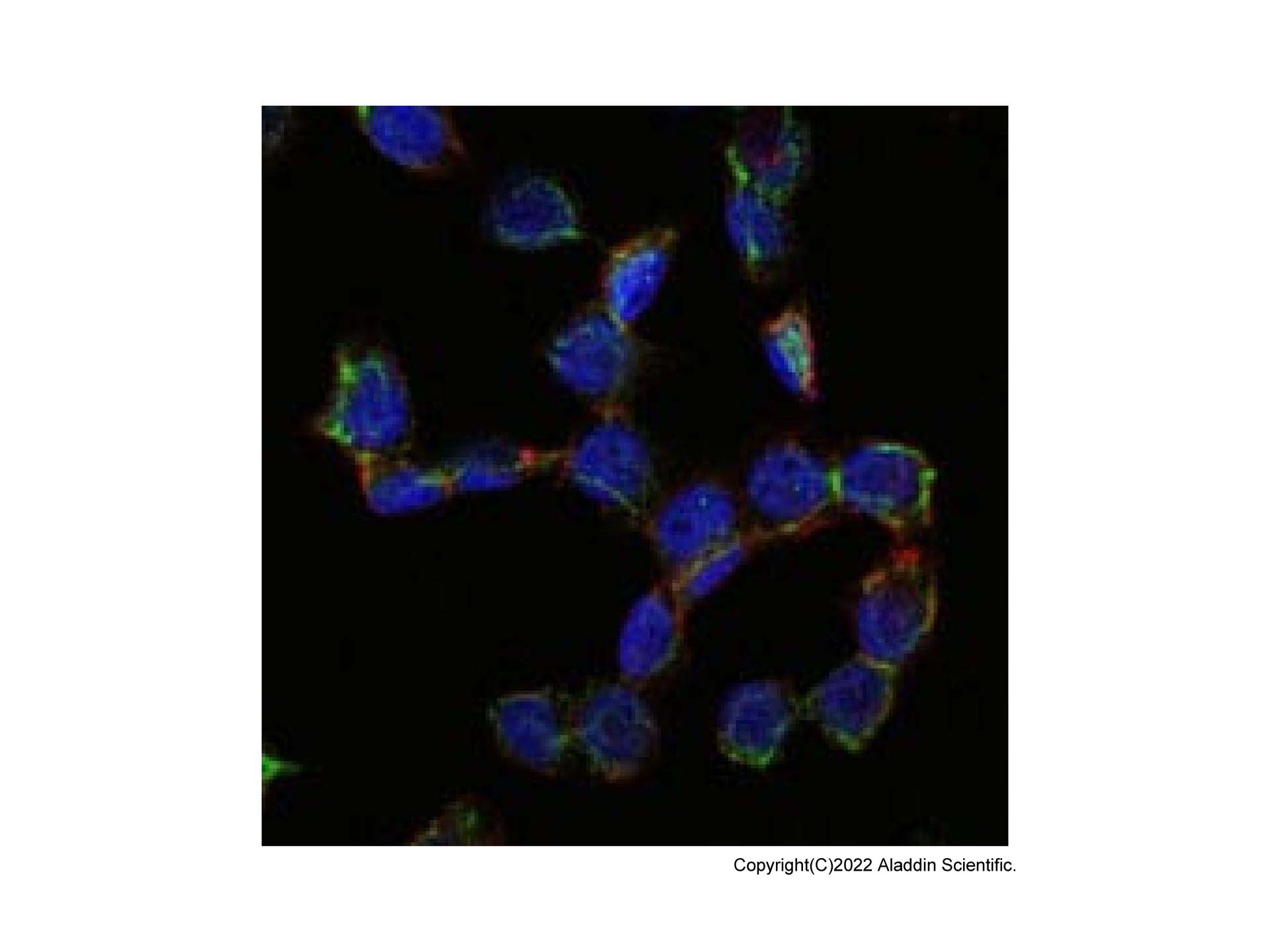
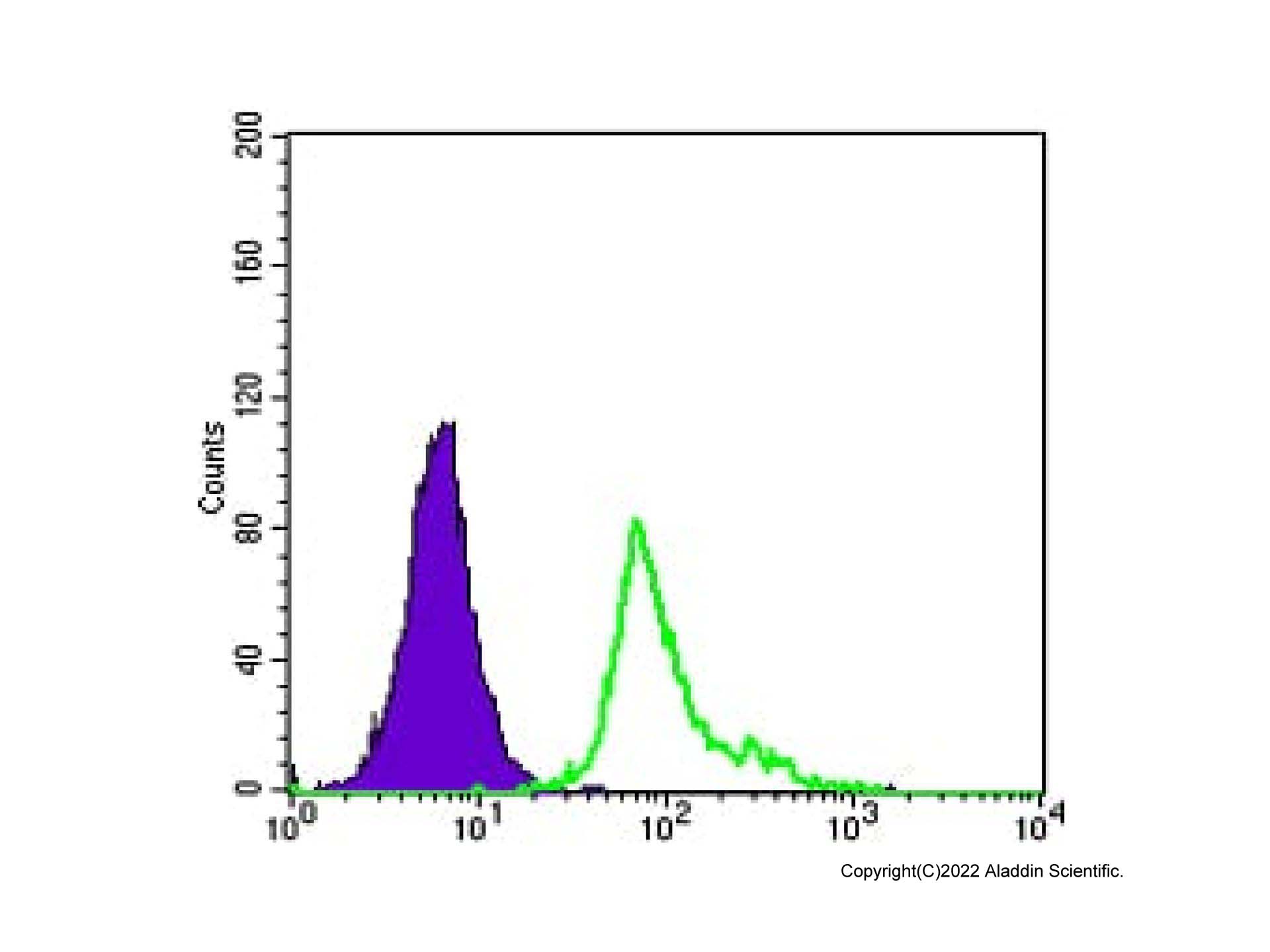
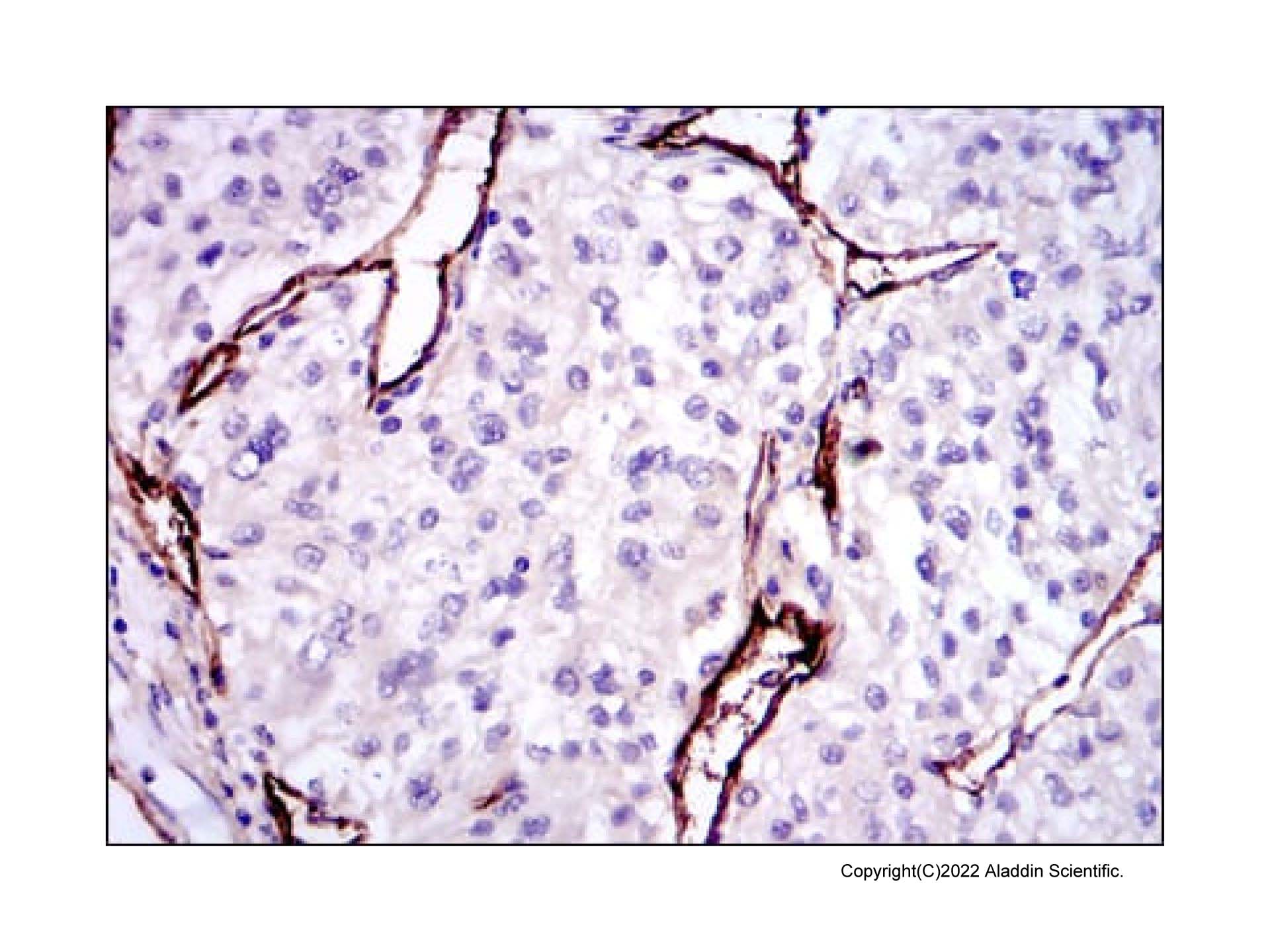
| 1. Cheifetz, S S and 6 more authors.. (1992) Endoglin is a component of the transforming growth factor-beta receptor system in human endothelial cells.. The Journal of biological chemistry, (25): [PMID:1326540] |
| 2. Gougos, A A and Letarte, M M.. (1990) Primary structure of endoglin, an RGD-containing glycoprotein of human endothelial cells.. The Journal of biological chemistry, (25): [PMID:1692830] |
| 3. McAllister, K A KA and 9 more authors.. (1994) Endoglin, a TGF-beta binding protein of endothelial cells, is the gene for hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia type 1.. Nature genetics, [PMID:7894484] |
| 4. Bellón, T T and 9 more authors.. (1993) Identification and expression of two forms of the human transforming growth factor-beta-binding protein endoglin with distinct cytoplasmic regions.. European journal of immunology, [PMID:8370410] |
| 5. Yamaguchi, H H, Azuma, H H, Shigekiyo, T T, Inoue, H H and Saito, S S.. (1997) A novel missense mutation in the endoglin gene in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.. Thrombosis and haemostasis, [PMID:9157574] |
| 6. Shovlin, C L CL, Hughes, J M JM, Scott, J J, Seidman, C E CE and Seidman, J G JG.. (1997) Characterization of endoglin and identification of novel mutations in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.. American journal of human genetics, [PMID:9245986] |
| 7. Gallione, C J CJ and 18 more authors.. (1998) Mutation and expression analysis of the endoglin gene in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia reveals null alleles.. Human mutation, [PMID:9554745] |
| 8. Pece-Barbara, N N, Cymerman, U U, Vera, S S, Marchuk, D A DA and Letarte, M M.. (1999) Expression analysis of four endoglin missense mutations suggests that haploinsufficiency is the predominant mechanism for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia type 1.. Human molecular genetics, [PMID:10545596] |
| 9. Cymerman, U U and 6 more authors.. (2000) Identification of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia type 1 in newborns by protein expression and mutation analysis of endoglin.. Pediatric research, [PMID:10625079] |
| 10. Gallione, C J CJ and 6 more authors.. (2000) Two common endoglin mutations in families with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia in the Netherlands Antilles: evidence for a founder effect.. Human genetics, [PMID:10982033] |
| 11. Lesca, Gaëtan G and 15 more authors.. (2004) Molecular screening of ALK1/ACVRL1 and ENG genes in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia in France.. Human mutation, [PMID:15024723] |
| 12. Humphray, S J SJ and 147 more authors.. (2004) DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 9.. Nature, (27): [PMID:15164053] |
| 13. Kuehl, Heidi K A HK and 6 more authors.. (2005) Hepatic manifestation is associated with ALK1 in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: identification of five novel ALK1 and one novel ENG mutations.. Human mutation, [PMID:15712270] |
| 14. Argyriou, Loukas L and 6 more authors.. (2006) Novel mutations in the ENG and ACVRL1 genes causing hereditary hemorrhagic teleangiectasia.. International journal of molecular medicine, [PMID:16525724] |
| 15. Bossler, Aaron D AD, Richards, Jennifer J, George, Cicily C, Godmilow, Lynn L and Ganguly, Arupa A.. (2006) Novel mutations in ENG and ACVRL1 identified in a series of 200 individuals undergoing clinical genetic testing for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT): correlation of genotype with phenotype.. Human mutation, [PMID:16752392] |
| 16. Meng, Qingjun Q and 10 more authors.. (2006) Identification of Tctex2beta, a novel dynein light chain family member that interacts with different transforming growth factor-beta receptors.. The Journal of biological chemistry, (1): [PMID:16982625] |
| 17. Lee, Nam Y NY and Blobe, Gerard C GC.. (2007) The interaction of endoglin with beta-arrestin2 regulates transforming growth factor-beta-mediated ERK activation and migration in endothelial cells.. The Journal of biological chemistry, (20): [PMID:17540773] |
| 18. Richards-Yutz, Jennifer J, Grant, Kathleen K, Chao, Elizabeth C EC, Walther, Susan E SE and Ganguly, Arupa A.. (2010) Update on molecular diagnosis of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.. Human genetics, [PMID:20414677] |
| 19. Castonguay, Roselyne R and 11 more authors.. (2011) Soluble endoglin specifically binds bone morphogenetic proteins 9 and 10 via its orphan domain, inhibits blood vessel formation, and suppresses tumor growth.. The Journal of biological chemistry, (26): [PMID:21737454] |
| 20. Alt, Aaron A and 8 more authors.. (2012) Structural and functional insights into endoglin ligand recognition and binding.. PloS one, [PMID:22347366] |
| 21. Nolan-Stevaux, Olivier O and 6 more authors.. (2012) Endoglin requirement for BMP9 signaling in endothelial cells reveals new mechanism of action for selective anti-endoglin antibodies.. PloS one, [PMID:23300529] |
| 22. Saito, Takako T and 7 more authors.. (2017) Structural Basis of the Human Endoglin-BMP9 Interaction: Insights into BMP Signaling and HHT1.. Cell reports, (30): [PMID:28564608] |